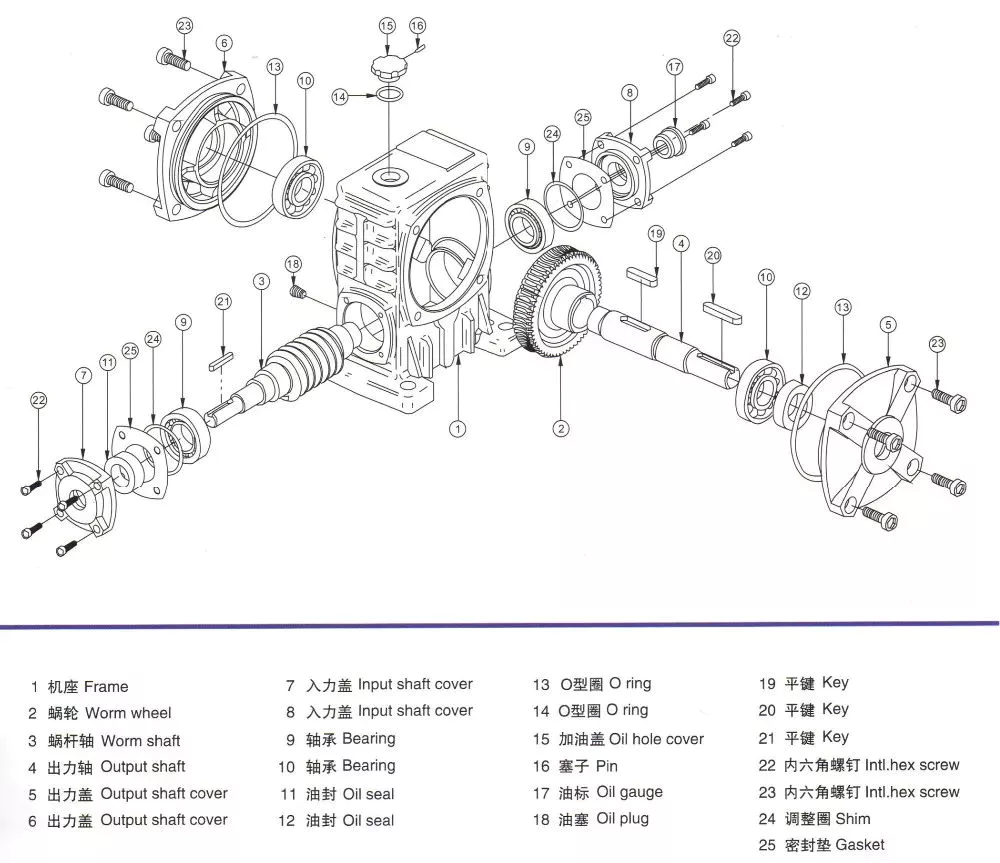
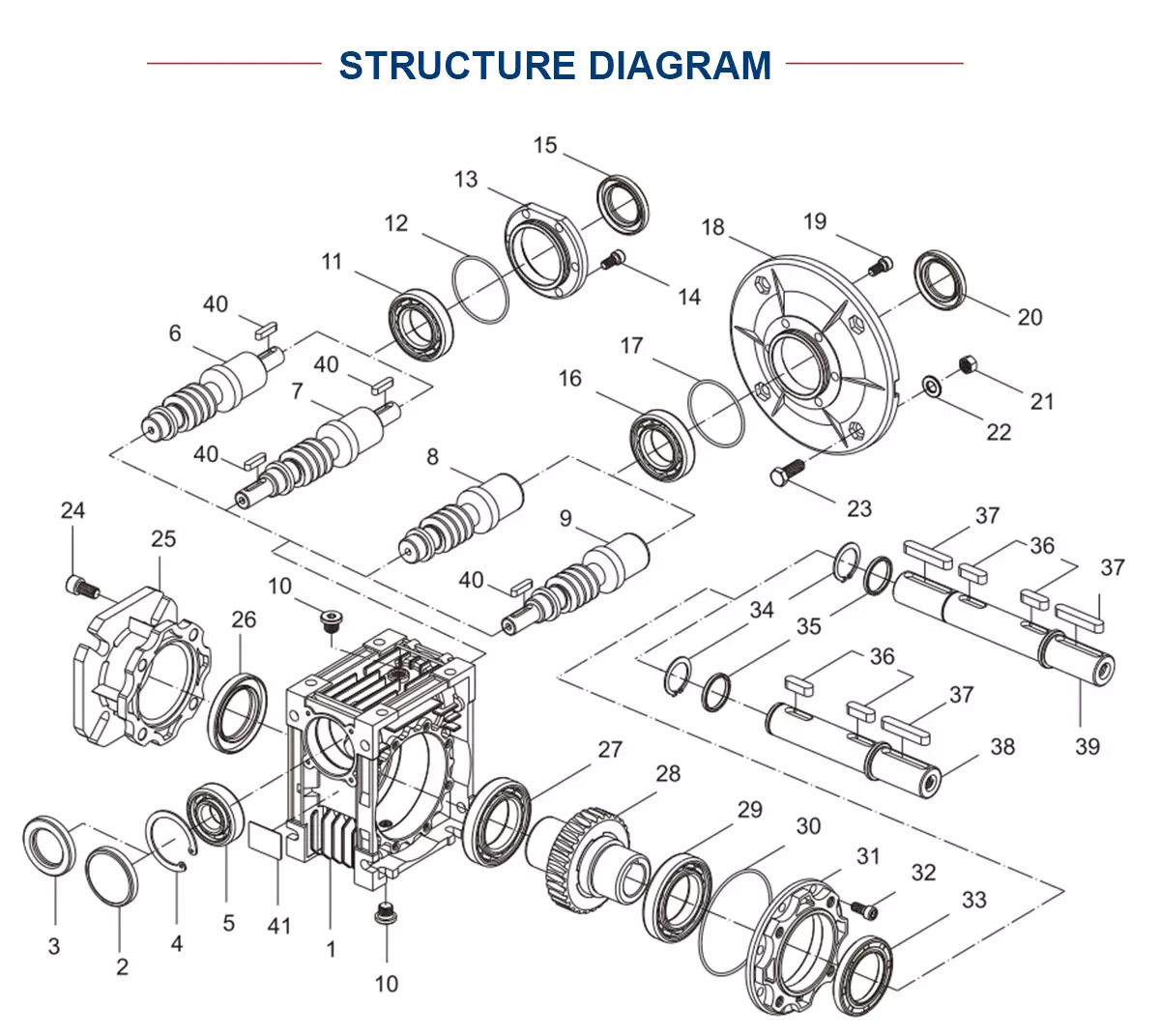
Product Description
Product Description:
1.Flexspline is a hollow flanging standard cylinder structure.
2.There is a large-diameter hollow shaft hole in the middle of the cam of the wave generator. The internal design of the reducer has a support bearing.
3.It has a fully sealed structure and is easy to install. It is very suitable for the occasions where the wire needs to be threaded from the center of the reducer.
Advantages:
The first:High precision,high torque
The second:dedicated technical personnel can be on-the-go to provide design solutions
The third:Factory direct sales fine workmanship durable quality assurance
The fourth:Product quality issues have a one-year warranty time, can be returned for replacement or repair
Company profile:
HangZhou CHINAMFG Technology Co., Ltd. established in 2014, is committed to the R & D plant of high-precision transmission components. At present, the annual production capacity can reach 45000 sets of harmonic reducers. We firmly believe in quality first. All links from raw materials to finished products are strictly supervised and controlled, which provides a CHINAMFG foundation for product quality. Our products are sold all over the country and abroad.
The harmonic reducer and other high-precision transmission components were independently developed by the company. Our company spends 20% of its sales every year on the research and development of new technologies in the industry. There are 5 people in R & D.
Our advantage is as below:
1.7 years of marketing experience
2. 5-person R & D team to provide you with technical support
3. It is sold at home and abroad and exported to Turkey and Ireland
4. The product quality is guaranteed with a one-year warranty
5. Products can be customized
Strength factory:
Our plant has an entire campus The number of workshops is around 300 Whether it’s from the production of raw materials and the procurement of raw materials to the inspection of finished products, we’re doing it ourselves. There is a complete production system
HST-III Parameter:
| Model | Speed ratio | Enter the rated torque at 2000r/min | Allowed CHINAMFG torque at start stop | The allowable maximum of the average load torque | Maximum torque is allowed in an instant | Allow the maximum speed to be entered | Average input speed is allowed | Back gap | design life | ||||
| NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | r / min | r / min | Arc sec | Hour | ||
| 14 | 50 | 6.2 | 0.6 | 20.7 | 2.1 | 7.9 | 0.7 | 40.3 | 4.1 | 7000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 10000 |
| 80 | 9 | 0.9 | 27 | 2.7 | 12.7 | 1.3 | 54.1 | 5.5 | |||||
| 100 | 9 | 0.9 | 32 | 3.3 | 12.7 | 1.3 | 62.1 | 6.3 | |||||
| 17 | 50 | 18.4 | 1.9 | 39 | 4 | 29.9 | 3 | 80.5 | 8.2 | 6500 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 25.3 | 2.6 | 49.5 | 5 | 31 | 3.2 | 100.1 | 10.2 | |||||
| 100 | 27.6 | 2.8 | 62 | 6.3 | 45 | 4.6 | 124.2 | 12.7 | |||||
| 20 | 50 | 28.8 | 2.9 | 64.4 | 6.6 | 39 | 4 | 112.7 | 11.5 | 5600 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 39.1 | 4 | 85 | 8.8 | 54 | 5.5 | 146.1 | 14.9 | |||||
| 100 | 46 | 4.7 | 94.3 | 9.6 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 120 | 46 | 4.7 | 100 | 10.2 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 160 | 46 | 4.7 | 100 | 10.2 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 25 | 50 | 44.9 | 4.6 | 113 | 11.5 | 63 | 6.5 | 213.9 | 21.8 | 4800 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 72.5 | 7.4 | 158 | 16.1 | 100 | 10.2 | 293.3 | 29.9 | |||||
| 100 | 77.1 | 7.9 | 181 | 18.4 | 124 | 12.7 | 326.6 | 33.3 | |||||
| 120 | 77.1 | 7.9 | 192 | 19.6 | 124 | 12.7 | 349.6 | 35.6 | |||||
| 32 | 50 | 87.4 | 8.9 | 248 | 25.3 | 124 | 12.7 | 439 | 44.8 | 4000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 135.7 | 13.8 | 350 | 35.6 | 192 | 19.6 | 653 | 66.6 | |||||
| 100 | 157.6 | 16.1 | 383 | 39.1 | 248 | 25.3 | 744 | 75.9 | |||||
| 40 | 100 | 308 | 37.2 | 660 | 67 | 432 | 44 | 1232 | 126.7 | 4000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
HSG Parameter:
| Model | Speed ratio | Enter the rated torque at 2000r/min | Allowed CHINAMFG torque at start stop | The allowable maximum of the average load torque | Maximum torque is allowed in an instant | Allow the maximum speed to be entered | Average input speed is allowed | Back gap | design life | ||||
| NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | r / min | r / min | Arc sec | Hour | ||
| 14 | 50 | 7 | 0.7 | 23 | 2.3 | 9 | 0.9 | 46 | 4.7 | 14000 | 8500 | ≤20 | 15000 |
| 80 | 10 | 1 | 30 | 3.1 | 14 | 1.4 | 61 | 6.2 | |||||
| 100 | 10 | 1 | 36 | 3.7 | 14 | 1.4 | 70 | 7.2 | |||||
| 17 | 50 | 21 | 2.1 | 44 | 4.5 | 34 | 3.4 | 91 | 9 | 10000 | 7300 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 29 | 2.9 | 56 | 5.7 | 35 | 3.6 | 113 | 12 | |||||
| 100 | 31 | 3.2 | 70 | 7.2 | 51 | 5.2 | 143 | 15 | |||||
| 20 | 50 | 33 | 3.3 | 73 | 7.4 | 44 | 4.5 | 127 | 13 | 10000 | 6500 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 44 | 4.5 | 96 | 9.8 | 61 | 6.2 | 165 | 17 | |||||
| 100 | 52 | 5.3 | 107 | 10.9 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 120 | 52 | 5.3 | 113 | 11.5 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 160 | 52 | 5.3 | 120 | 12.2 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 25 | 50 | 51 | 5.2 | 127 | 13 | 72 | 7.3 | 242 | 25 | 7500 | 5600 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 82 | 8.4 | 178 | 18 | 113 | 12 | 332 | 34 | |||||
| 100 | 87 | 8.9 | 204 | 21 | 140 | 14 | 369 | 38 | |||||
| 120 | 87 | 8.9 | 217 | 22 | 140 | 14 | 395 | 40 | |||||
| 32 | 50 | 99 | 10 | 281 | 29 | 140 | 14 | 497 | 51 | 7000 | 4800 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 153 | 16 | 395 | 40 | 217 | 22 | 738 | 75 | |||||
| 100 | 178 | 18 | 433 | 44 | 281 | 29 | 841 | 86 | |||||
| 40 | 100 | 345 | 35 | 738 | 75 | 484 | 49 | 1400 | 143 | 5600 | 4000 | ≤20 | 20000 |
Exhibition:
Application case:
FQA:
Q: What should I provide when I choose gearbox/speed reducer?
A: The best way is to provide the motor drawing with parameter. Our engineer will check and recommend the most suitable gearbox model for your refer.
Or you can also provide below specification as well:
1) Type, model and torque.
2) Ratio or output speed
3) Working condition and connection method
4) Quality and installed machine name
5) Input mode and input speed
6) Motor brand model or flange and motor shaft size
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | 90 Degree |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Gear Shape: | Cylindrical Gear |
| Step: | Single-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How does backlash affect the performance of gear drives?
Backlash in gear drives can have significant effects on performance. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Accuracy and Positioning:
– Backlash can introduce positional errors and affect the accuracy of motion transmission in gear drives.
– When there is backlash, the motion of the driven gear may not immediately respond to changes in the driving gear’s direction or position.
– This can result in imprecise positioning and reduced accuracy, particularly in applications that require high precision, such as CNC machines or robotics.
2. Reversal and Repeatability:
– Backlash can cause issues during gear drive reversal or when changing the direction of motion.
– In systems with significant backlash, the gears need to overcome the backlash before initiating motion in the opposite direction.
– This can lead to delays, jerky movements, and reduced repeatability, impacting the overall performance and efficiency of the system.
3. Vibrations and Noise:
– Backlash can contribute to vibrations and noise in gear drives.
– Rapid changes in direction or sudden load reversals can cause the gear teeth to impact each other, resulting in impacts and vibrations.
– These impacts can generate noise and increase wear and fatigue on the gear teeth, affecting the overall lifespan and reliability of the gear drive.
4. System Stiffness and Response:
– Backlash can reduce the system stiffness and responsiveness of gear drives.
– In applications where precise control is required, such as in high-speed machining or servo systems, backlash can lead to system instability and reduced control performance.
– The presence of backlash can lead to delays, overshoot, and poor dynamic response, limiting the overall system performance.
5. Efficiency and Power Transmission:
– Backlash can result in power losses and reduced efficiency in gear drives.
– During gear engagement, the presence of backlash can cause a momentary disengagement between the gear teeth, leading to energy loss and reduced power transmission efficiency.
– This is particularly important in applications where power efficiency is critical, such as in automotive transmissions or high-torque machinery.
6. Wear and Fatigue:
– Backlash can accelerate wear and fatigue on gear teeth.
– The impact and sliding motions between the gear teeth during reversal or changes in direction can cause additional stress and wear.
– Over time, excessive backlash can lead to increased tooth wear, decreased tooth profile accuracy, and reduced overall gear drive lifespan.
Minimizing backlash in gear drives is crucial for maintaining accuracy, repeatability, efficiency, and overall performance. Techniques such as proper gear design, precise manufacturing tolerances, and gear mesh optimization can help reduce backlash and mitigate its negative effects. However, it’s important to strike a balance because eliminating backlash entirely can lead to other issues, such as binding or jamming. The optimal level of backlash depends on the specific application and performance requirements of the gear drive system.

What is the role of gear drives in automotive transmissions?
Gear drives play a crucial role in automotive transmissions. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Speed and Torque Conversion:
– Automotive transmissions use gear drives to convert the engine’s rotational speed and torque into the appropriate output for the wheels.
– By selecting different gear ratios, gear drives enable the transmission to adjust the speed and torque delivered to the wheels based on driving conditions and desired performance.
2. Gear Shifting:
– Gear drives facilitate gear shifting, allowing the driver to select different gear ratios to match the vehicle’s speed and load requirements.
– Depending on the transmission type (manual or automatic), gear drives are responsible for engaging and disengaging the gears during gear shifting operations.
3. Power Transmission:
– Gear drives transmit power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move.
– They transfer torque from the engine’s crankshaft to the transmission output shaft, which is connected to the wheels through the drivetrain.
4. Forward and Reverse Operation:
– Gear drives in automotive transmissions allow the vehicle to move both forward and backward.
– By engaging different gear combinations, the transmission can reverse the direction of power flow, enabling the vehicle to go in reverse.
5. Gear Reduction and Overdrive:
– Gear drives in transmissions provide gear reduction or overdrive capabilities.
– Gear reduction allows the engine to operate at higher RPMs while reducing the output speed, providing more torque for climbing steep inclines or towing heavy loads.
– Overdrive gears, on the other hand, allow the engine to operate at lower RPMs, reducing fuel consumption and engine wear during highway cruising.
6. Synchronizing and Noise Reduction:
– In manual transmissions, gear drives incorporate synchronizer mechanisms to facilitate smooth gear engagements and minimize gear clash.
– These synchronizers match the speeds of the gears before engagement, reducing wear on the gear teeth and enhancing shifting comfort.
– Gear drives can also incorporate noise reduction measures, such as helical or hypoid gears, to minimize gear noise and vibration during operation.
Overall, gear drives in automotive transmissions are essential for speed and torque conversion, gear shifting, power transmission, and enabling the vehicle to move in both forward and reverse directions. They provide the necessary mechanical advantage and flexibility to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and driving dynamics, making them a fundamental component in the operation of automobiles.
How do you calculate the gear ratio in a gear drive?
Calculating the gear ratio in a gear drive involves determining the relationship between the number of teeth on the driving gear (pinion) and the number of teeth on the driven gear. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The gear ratio is defined as the ratio of the number of teeth on the driven gear to the number of teeth on the driving gear. It represents the speed or torque multiplication or reduction achieved by the gear drive.
The gear ratio (GR) can be calculated using the following formula:
GR = Number of teeth on driven gear / Number of teeth on driving gear
For example, consider a gear drive with a driving gear (pinion) having 20 teeth and a driven gear having 60 teeth. The gear ratio can be calculated as follows:
GR = 60 (driven gear) / 20 (driving gear) = 3
In this case, the gear ratio is 3:1, indicating that for every three revolutions of the driving gear, the driven gear completes one revolution. This represents a speed reduction, with the driven gear rotating at one-third the speed of the driving gear.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio can be expressed in different formats, such as a decimal, fraction, or as a ratio. The choice of representation depends on the specific requirements and conventions of the gear drive application.
Additionally, it’s worth mentioning that gear drives can have multiple gears arranged in series or parallel, forming gear trains. In such cases, the overall gear ratio is calculated by multiplying the individual gear ratios of each gear pair in the train.
When designing or selecting gear drives, calculating the gear ratio is essential for determining the speed reduction or increase and torque amplification provided by the gear system. It enables engineers and designers to match the gear drive to the desired operational requirements of the mechanical system.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06
