Product Description
Product Description:
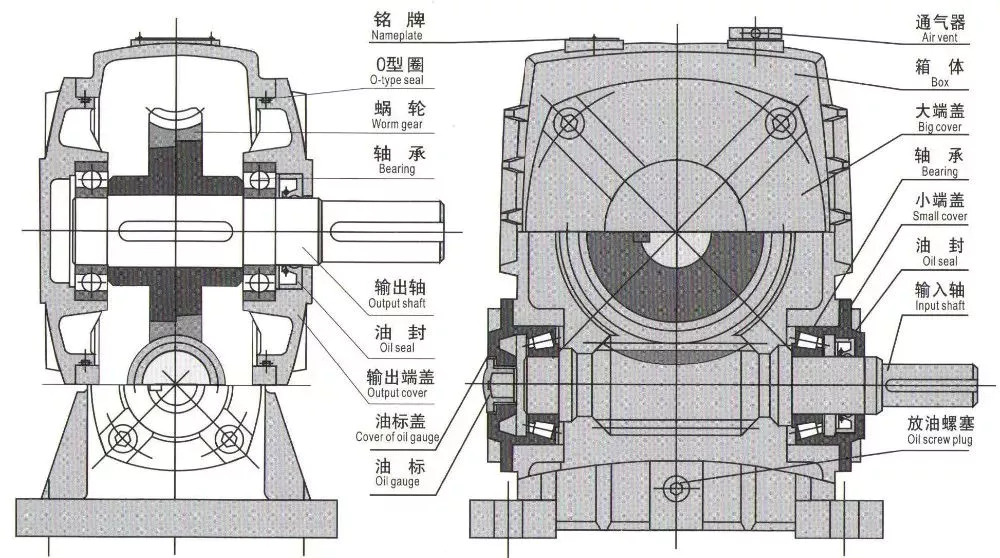
1.Flexspline is a hollow flanging standard cylinder structure.
2.There is a large-diameter hollow shaft hole in the middle of the cam of the wave generator. The internal design of the reducer has a support bearing.
3.It has a fully sealed structure and is easy to install. It is very suitable for the occasions where the wire needs to be threaded from the center of the reducer.
Advantages:
The first:High precision,high torque
The second:dedicated technical personnel can be on-the-go to provide design solutions
The third:Factory direct sales fine workmanship durable quality assurance
The fourth:Product quality issues have a one-year warranty time, can be returned for replacement or repair
Company profile:
HangZhou CHINAMFG Technology Co., Ltd. established in 2014, is committed to the R & D plant of high-precision transmission components. At present, the annual production capacity can reach 45000 sets of harmonic reducers. We firmly believe in quality first. All links from raw materials to finished products are strictly supervised and controlled, which provides a CHINAMFG foundation for product quality. Our products are sold all over the country and abroad.
The harmonic reducer and other high-precision transmission components were independently developed by the company. Our company spends 20% of its sales every year on the research and development of new technologies in the industry. There are 5 people in R & D.
Our advantage is as below:
1.7 years of marketing experience
2. 5-person R & D team to provide you with technical support
3. It is sold at home and abroad and exported to Turkey and Ireland
4. The product quality is guaranteed with a one-year warranty
5. Products can be customized
Strength factory:
Our plant has an entire campus The number of workshops is around 300 Whether it’s from the production of raw materials and the procurement of raw materials to the inspection of finished products, we’re doing it ourselves. There is a complete production system
HST-III Parameter:
| Model | Speed ratio | Enter the rated torque at 2000r/min | Allowed CHINAMFG torque at start stop | The allowable maximum of the average load torque | Maximum torque is allowed in an instant | Allow the maximum speed to be entered | Average input speed is allowed | Back gap | design life | ||||
| NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | r / min | r / min | Arc sec | Hour | ||
| 14 | 50 | 6.2 | 0.6 | 20.7 | 2.1 | 7.9 | 0.7 | 40.3 | 4.1 | 7000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 10000 |
| 80 | 9 | 0.9 | 27 | 2.7 | 12.7 | 1.3 | 54.1 | 5.5 | |||||
| 100 | 9 | 0.9 | 32 | 3.3 | 12.7 | 1.3 | 62.1 | 6.3 | |||||
| 17 | 50 | 18.4 | 1.9 | 39 | 4 | 29.9 | 3 | 80.5 | 8.2 | 6500 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 25.3 | 2.6 | 49.5 | 5 | 31 | 3.2 | 100.1 | 10.2 | |||||
| 100 | 27.6 | 2.8 | 62 | 6.3 | 45 | 4.6 | 124.2 | 12.7 | |||||
| 20 | 50 | 28.8 | 2.9 | 64.4 | 6.6 | 39 | 4 | 112.7 | 11.5 | 5600 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 39.1 | 4 | 85 | 8.8 | 54 | 5.5 | 146.1 | 14.9 | |||||
| 100 | 46 | 4.7 | 94.3 | 9.6 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 120 | 46 | 4.7 | 100 | 10.2 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 160 | 46 | 4.7 | 100 | 10.2 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 25 | 50 | 44.9 | 4.6 | 113 | 11.5 | 63 | 6.5 | 213.9 | 21.8 | 4800 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 72.5 | 7.4 | 158 | 16.1 | 100 | 10.2 | 293.3 | 29.9 | |||||
| 100 | 77.1 | 7.9 | 181 | 18.4 | 124 | 12.7 | 326.6 | 33.3 | |||||
| 120 | 77.1 | 7.9 | 192 | 19.6 | 124 | 12.7 | 349.6 | 35.6 | |||||
| 32 | 50 | 87.4 | 8.9 | 248 | 25.3 | 124 | 12.7 | 439 | 44.8 | 4000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 135.7 | 13.8 | 350 | 35.6 | 192 | 19.6 | 653 | 66.6 | |||||
| 100 | 157.6 | 16.1 | 383 | 39.1 | 248 | 25.3 | 744 | 75.9 | |||||
| 40 | 100 | 308 | 37.2 | 660 | 67 | 432 | 44 | 1232 | 126.7 | 4000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
HSG Parameter:
| Model | Speed ratio | Enter the rated torque at 2000r/min | Allowed CHINAMFG torque at start stop | The allowable maximum of the average load torque | Maximum torque is allowed in an instant | Allow the maximum speed to be entered | Average input speed is allowed | Back gap | design life | ||||
| NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | r / min | r / min | Arc sec | Hour | ||
| 14 | 50 | 7 | 0.7 | 23 | 2.3 | 9 | 0.9 | 46 | 4.7 | 14000 | 8500 | ≤20 | 15000 |
| 80 | 10 | 1 | 30 | 3.1 | 14 | 1.4 | 61 | 6.2 | |||||
| 100 | 10 | 1 | 36 | 3.7 | 14 | 1.4 | 70 | 7.2 | |||||
| 17 | 50 | 21 | 2.1 | 44 | 4.5 | 34 | 3.4 | 91 | 9 | 10000 | 7300 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 29 | 2.9 | 56 | 5.7 | 35 | 3.6 | 113 | 12 | |||||
| 100 | 31 | 3.2 | 70 | 7.2 | 51 | 5.2 | 143 | 15 | |||||
| 20 | 50 | 33 | 3.3 | 73 | 7.4 | 44 | 4.5 | 127 | 13 | 10000 | 6500 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 44 | 4.5 | 96 | 9.8 | 61 | 6.2 | 165 | 17 | |||||
| 100 | 52 | 5.3 | 107 | 10.9 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 120 | 52 | 5.3 | 113 | 11.5 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 160 | 52 | 5.3 | 120 | 12.2 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 25 | 50 | 51 | 5.2 | 127 | 13 | 72 | 7.3 | 242 | 25 | 7500 | 5600 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 82 | 8.4 | 178 | 18 | 113 | 12 | 332 | 34 | |||||
| 100 | 87 | 8.9 | 204 | 21 | 140 | 14 | 369 | 38 | |||||
| 120 | 87 | 8.9 | 217 | 22 | 140 | 14 | 395 | 40 | |||||
| 32 | 50 | 99 | 10 | 281 | 29 | 140 | 14 | 497 | 51 | 7000 | 4800 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 153 | 16 | 395 | 40 | 217 | 22 | 738 | 75 | |||||
| 100 | 178 | 18 | 433 | 44 | 281 | 29 | 841 | 86 | |||||
| 40 | 100 | 345 | 35 | 738 | 75 | 484 | 49 | 1400 | 143 | 5600 | 4000 | ≤20 | 20000 |
Exhibition:
Application case:
FQA:
Q: What should I provide when I choose gearbox/speed reducer?
A: The best way is to provide the motor drawing with parameter. Our engineer will check and recommend the most suitable gearbox model for your refer.
Or you can also provide below specification as well:
1) Type, model and torque.
2) Ratio or output speed
3) Working condition and connection method
4) Quality and installed machine name
5) Input mode and input speed
6) Motor brand model or flange and motor shaft size
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | 90 Degree |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Gear Shape: | Cylindrical Gear |
| Step: | Single-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do gear drives work in robotic and automated systems?
Gear drives play a crucial role in robotic and automated systems by transmitting motion and power between different components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gear drives work in these systems:
1. Power Transmission:
– In robotic and automated systems, gear drives are used to transmit power from motors to various mechanical components.
– Electric motors provide rotational motion, which is converted into linear or angular motion by the gear drive.
– The gear drive consists of a set of gears with different sizes and configurations that mesh together to transfer torque and speed.
2. Speed and Torque Conversion:
– Gear drives allow for the conversion of speed and torque between the motor and the driven components.
– By using gears with different sizes (varying number of teeth), the gear drive can change the rotational speed and torque output.
– For example, a gear drive with a larger gear driving a smaller gear will increase the torque while reducing the speed, and vice versa.
3. Motion Control:
– Gear drives enable precise motion control in robotic and automated systems.
– By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the gear drive can control the speed and position of the driven components.
– Gear drives can be used to achieve smooth and accurate movements, such as in robot arms, conveyor systems, or CNC machines.
4. Reducing Inertia:
– Inertia refers to an object’s resistance to changes in motion.
– Gear drives can help reduce the overall inertia in robotic and automated systems.
– By using smaller gears, the gear drive can reduce the inertia of the driven components, allowing for faster and more responsive movements.
5. Backlash Compensation:
– Backlash refers to the slight play or clearance between gear teeth, which can result in a loss of accuracy and precision.
– Gear drives in robotic and automated systems often incorporate backlash compensation mechanisms to minimize this issue.
– These mechanisms can include preloading the gears or using anti-backlash gears to eliminate or reduce the effects of backlash.
6. Load Distribution:
– In complex robotic systems, multiple gear drives are often used to distribute the load and share the torque among different components.
– This distribution of load helps prevent overloading of individual gear drives and ensures a balanced operation of the system.
7. Redundancy:
– Some robotic and automated systems incorporate redundant gear drives to enhance reliability and fault tolerance.
– Redundant gear drives can provide backup functionality in case of failure or allow for continued operation with reduced performance in the event of a single gear drive failure.
Overall, gear drives are essential components in robotic and automated systems, enabling power transmission, motion control, speed and torque conversion, and load distribution. The specific design and configuration of gear drives in these systems depend on the application requirements, desired performance, and system constraints.

What innovations are currently shaping the future of gear drives?
Several innovations are currently shaping the future of gear drives. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Advanced Materials:
– The development and utilization of advanced materials are revolutionizing gear drive technology.
– High-performance materials, such as carbon composites and advanced polymers, offer improved strength, durability, and weight reduction compared to traditional metal gears.
– These materials enable the design of more compact and lightweight gear drives with enhanced efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
2. Additive Manufacturing:
– Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is transforming the manufacturing process of gear drives.
– It allows for complex and optimized designs, including internal structures and intricate geometries, that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
– Additive manufacturing enables the production of customized gear drives with improved performance, reduced weight, and faster prototyping.
3. Smart Gear Drives:
– The integration of sensors, actuators, and control systems is enabling the development of smart gear drives.
– Smart gear drives can monitor operating conditions, collect data, and adjust their performance in real-time.
– They offer advantages such as condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, fault detection, and adaptive control, leading to increased reliability, efficiency, and lifespan.
4. Digitalization and Connectivity:
– The digitalization of gear drive systems through the Internet of Things (IoT) and connectivity technologies is transforming their functionality.
– Connected gear drives can communicate with other components, control systems, and central monitoring platforms, allowing for remote monitoring, optimization, and diagnostics.
– Digitalization enables advanced analytics, machine learning, and predictive algorithms to optimize gear drive performance, energy efficiency, and maintenance scheduling.
5. Gearless Systems:
– Gearless systems are emerging as an innovative alternative to traditional gear drives in certain applications.
– In these systems, direct drive technologies, such as magnetic gears or direct-coupled generators, eliminate the need for gear transmission.
– Gearless systems offer advantages such as higher efficiency, reduced maintenance requirements, compact size, and improved reliability.
6. Eco-Friendly Lubricants:
– The development of eco-friendly lubricants is influencing the future of gear drives.
– Environmentally friendly lubricants, such as bio-based or synthetic oils with reduced toxicity and improved biodegradability, are being used to enhance gear drive performance while minimizing environmental impact.
– These lubricants offer benefits such as extended gear life, reduced friction, and improved energy efficiency.
These innovations are driving advancements in gear drive technology, leading to more efficient, reliable, and sustainable systems. They are shaping the future of gear drives by improving performance, reducing weight and size, enhancing connectivity and control, and minimizing environmental impact.
What are the common applications of gear drives in industry?
Gear drives find widespread applications in various industries due to their ability to efficiently transmit power and control speed. Here’s a detailed explanation of the common applications of gear drives in industry:
1. Automotive Industry:
– Gear drives are extensively used in automotive applications, such as transmissions and differential drives.
– They enable speed reduction, torque multiplication, and efficient power transmission in vehicles.
– Gear drives in automobiles help control speed ranges, enable gear shifting, and deliver power to the wheels.
2. Industrial Machinery:
– Gear drives are widely employed in various industrial machinery, including conveyors, mixers, pumps, and machine tools.
– They provide speed reduction or increase, torque amplification, and precise speed control in industrial equipment.
– Gear drives ensure efficient power transmission, synchronization of rotating components, and reliable operation of machinery.
3. Robotics and Automation:
– Gear drives play a critical role in robotics and automated systems for precision motion control.
– They provide speed reduction, torque amplification, and accurate positioning in robotic arms, joints, and manipulators.
– Gear drives enable smooth and precise movement in automated assembly lines, CNC machines, and other robotic applications.
4. Aerospace and Aviation:
– Gear drives are utilized in aerospace and aviation applications, such as aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and control mechanisms.
– They facilitate power transmission, speed control, and torque conversion in aircraft components.
– Gear drives in aviation require lightweight and high-strength materials to meet the demands of aircraft performance.
5. Energy and Power Generation:
– Gear drives are employed in power generation applications, including wind turbines, hydroelectric turbines, and steam turbines.
– They enable speed reduction or increase to match the rotational speed requirements of generators and power transmission systems.
– Gear drives play a vital role in efficient energy conversion and transmission in renewable energy and conventional power plants.
6. Mining and Construction:
– Gear drives are utilized in heavy machinery used in mining, construction, and earthmoving operations.
– They enable power transmission, speed reduction, and torque amplification in excavators, bulldozers, and dump trucks.
– Gear drives in mining and construction machinery withstand high loads, shock, and harsh operating conditions.
These are just a few examples of the common applications of gear drives in industry. Gear drives are versatile and can be found in various other sectors like marine, agricultural machinery, material handling, and more. The specific design, material selection, and configuration of gear drives depend on the requirements of the application, including load capacity, speed range, torque demands, and environmental conditions.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06
